-
2,98 kW saulės elektrinės Jinko 425 REZERVACIJA
1x
100,00 €
-
8,08 kW saulės elektrinės Jinko 425 REZERVACIJA
1x
100,00 €
-
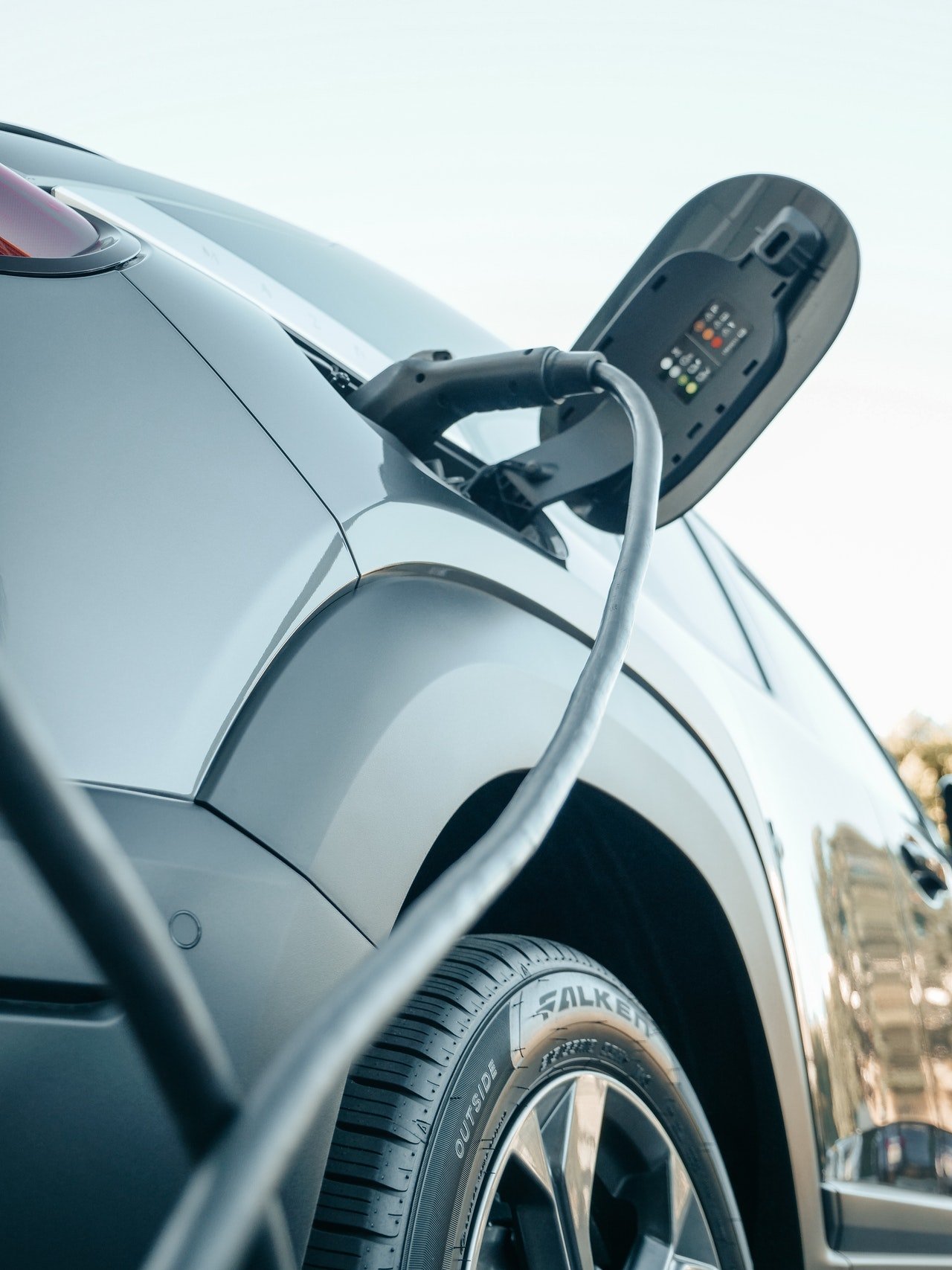
2,84 kW on- roof solar power plant DIY
1x
3300,00 €
-
15,39 kW ramming on- ground solar power plant DIY
1x
10400,00 €
Total:13900,00 €